
- Posted
- Categories
-
- OpenSAFELY
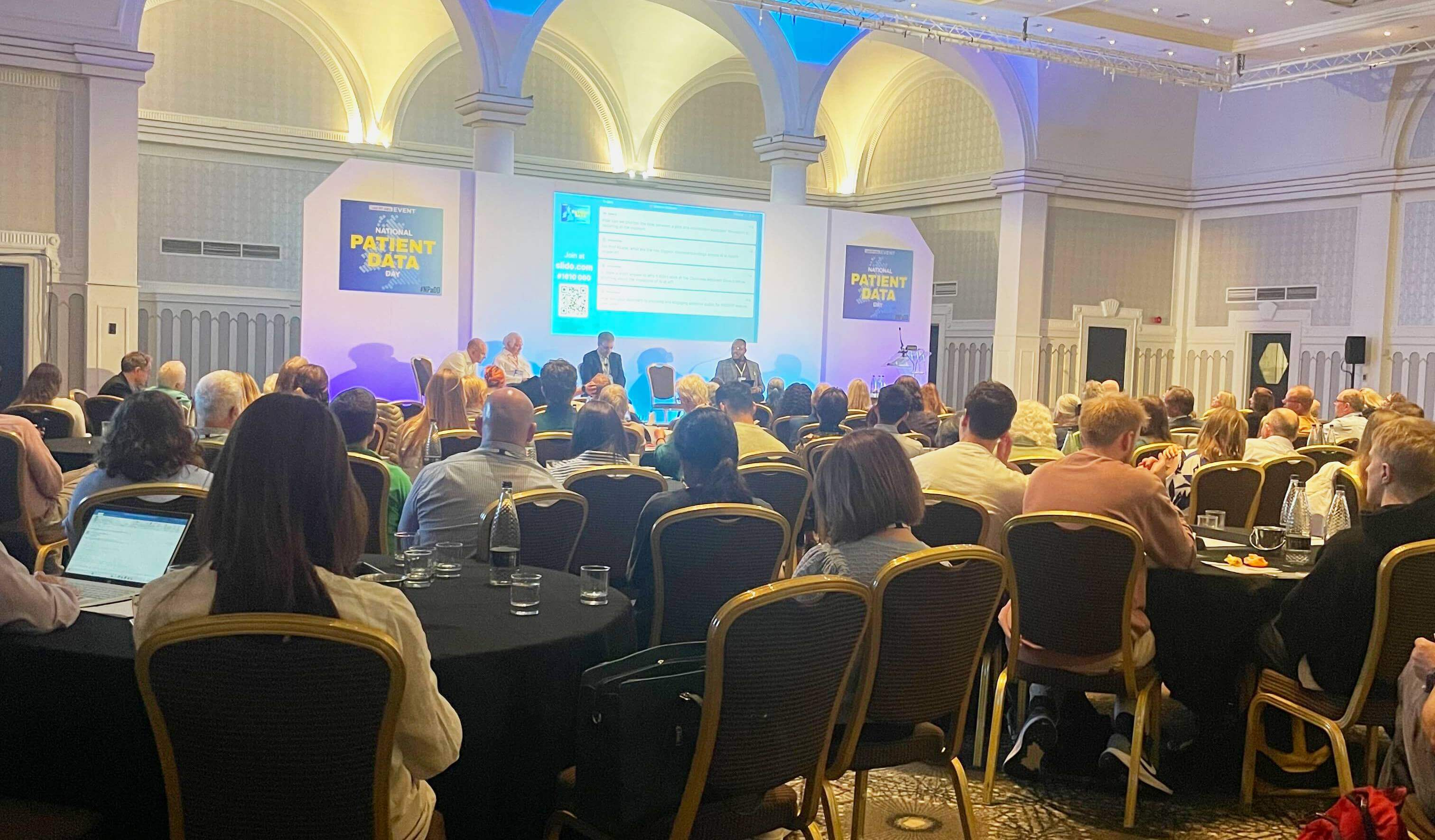
OpenSAFELY at the National Patient Data Day in Leeds
On the 24th June 2025, OpenSAFELY had the privilege of running a booth at the National Patient Data Day in Leeds!
OpenSAFELY is a new secure analytics platform for electronic health records in the NHS, created to deliver urgent results during the global COVID-19 emergency.
OpenSAFELY is a new secure analytics platform for electronic health records in the NHS, created to deliver urgent results during the global COVID-19 emergency. It is now successfully delivering analyses across more than 58 million patients’ full pseudonymised primary care NHS records, with more to follow shortly. All our analytic software is open for security review, scientific review, and re-use. OpenSAFELY uses a new model for enhanced security and timely access to data: we don’t transport large volumes of potentially disclosive pseudonymised patient data outside of the secure environments managed by the electronic health record software company; instead, trusted analysts can run large scale computation across near real-time pseudonymised patient records inside the data centre of the electronic health records software company. This pragmatic and secure approach allowed us to deliver our first analyses in just five weeks from project start.
Find out more about how OpenSAFELY works in this blog or read our papers and other blog posts, follow us on Twitter, or visit the website to find out more.
This study investigated patient characteristics associated with clinically coded long COVID from 29 January 2020 to 31 March 2022.
Status: Published
This study evaluated the effectiveness of the 2022 autumn COVID-19 booster campaign in 50 year olds in England using a regression discontinuity design.
Status: Published
This study used the National Waiting List Minimum Dataset linked with GP data to quantify the impact of waiting times on opioid prescribing during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Status: Preprint
This study investigated clinical coding used to support remote pulse oximetry services, with breakdown by regional, clinical and demographic subgroups.
Status: Preprint

On the 24th June 2025, OpenSAFELY had the privilege of running a booth at the National Patient Data Day in Leeds!

Office hours, coding meetups and more! Come and talk to other OpenSAFELY users.
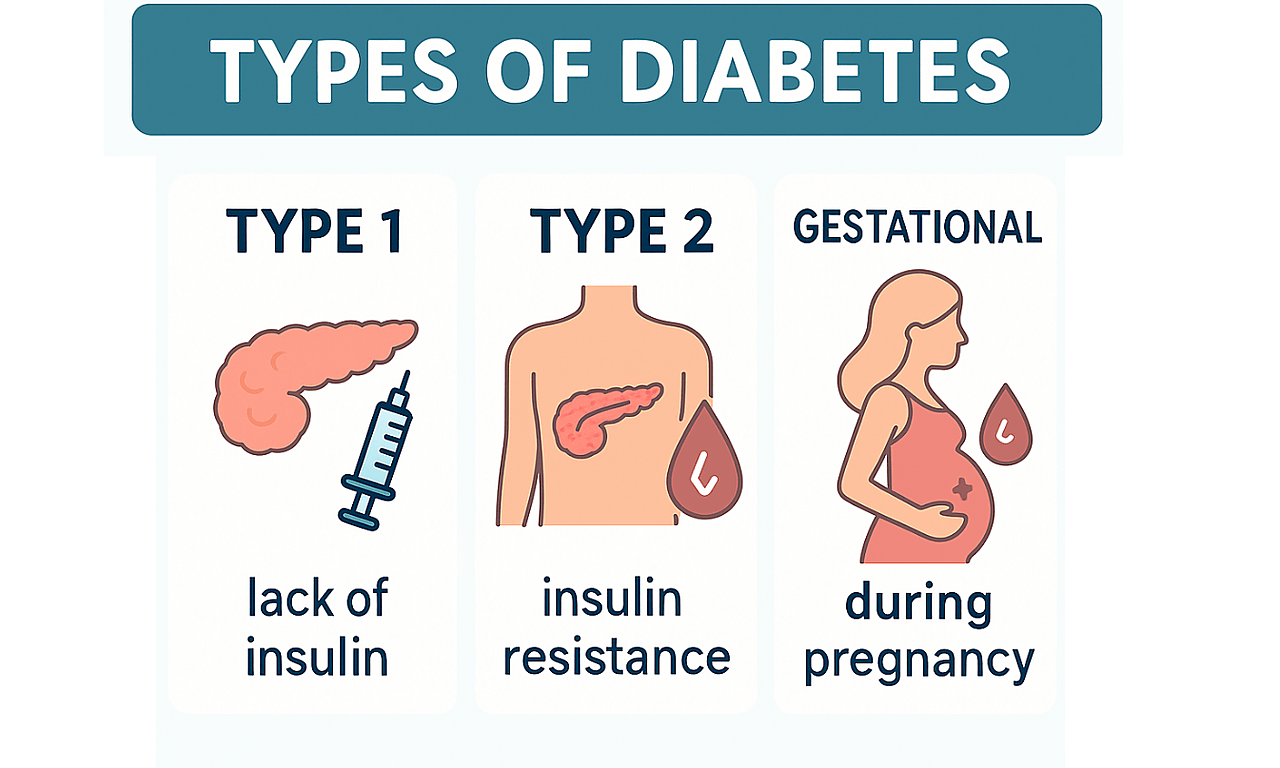
Together with collaborators in Bristol and at the Bennett Institute, we created a reusable action called ‘diabetes-algo’. Here is what it does.
Our tech team has been making improvements to OpenCodelists! What’s new?