Measuring anticoagulant use in secondary care using OpenPrescribing Hospitals: Part 3
- Posted:
- Written by:
- Categories:

This article is part of a series: Anticoagulant Use in NHS Hospitals in England
- Measuring anticoagulant use in secondary care using OpenPrescribing Hospitals: Part 1
- Measuring anticoagulant use in secondary care using OpenPrescribing Hospitals: Part 2
- Measuring anticoagulant use in secondary care using OpenPrescribing Hospitals: Part 3
In this 3 part blog series, Vicky Speed, clinical informatician at the Bennett Institute and specialist anticoagulation pharmacist at King’s College Hospital in London describes how OpenPrescribing Hospitals can be used to look at anticoagulant use in hospital trusts in England.
The blogs will describe analyses possible using OpenPrescribing Hospitals and tips for using the platform for:
- Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)
- Direct oral anticoagulants
- Vitamin K antagonists
Part 3 - Vitamin K antagonists on OpenPrescribing Hospitals
Did you know? There has been a ~50% reduction in vitamin K antagonist use in hospital trusts in England between January 2019 and January 2025. (OpenPrescribing Hospitals - July 2025)
What are vitamin K antagonists?
Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) belong to a group of medicines called anticoagulants (blood thinners). VKAs are mostly used to prevent strokes in patients with atrial fibrillation, treat blood clots, and to prevent clots in patients with metal heart valves. Warfarin is the most common VKA in use in NHS hospital trusts in England >98% (July 2025).
Use of VKAs is declining
Since January 2019, there has been a ~50% reduction in VKAs issued in NHS hospitals in England. You can check out use nationally, and by region or ICB on OpenPrescribing Hospitals. To see the breakdown of numbers at each of these geographical levels, check out the summary tables below the charts.
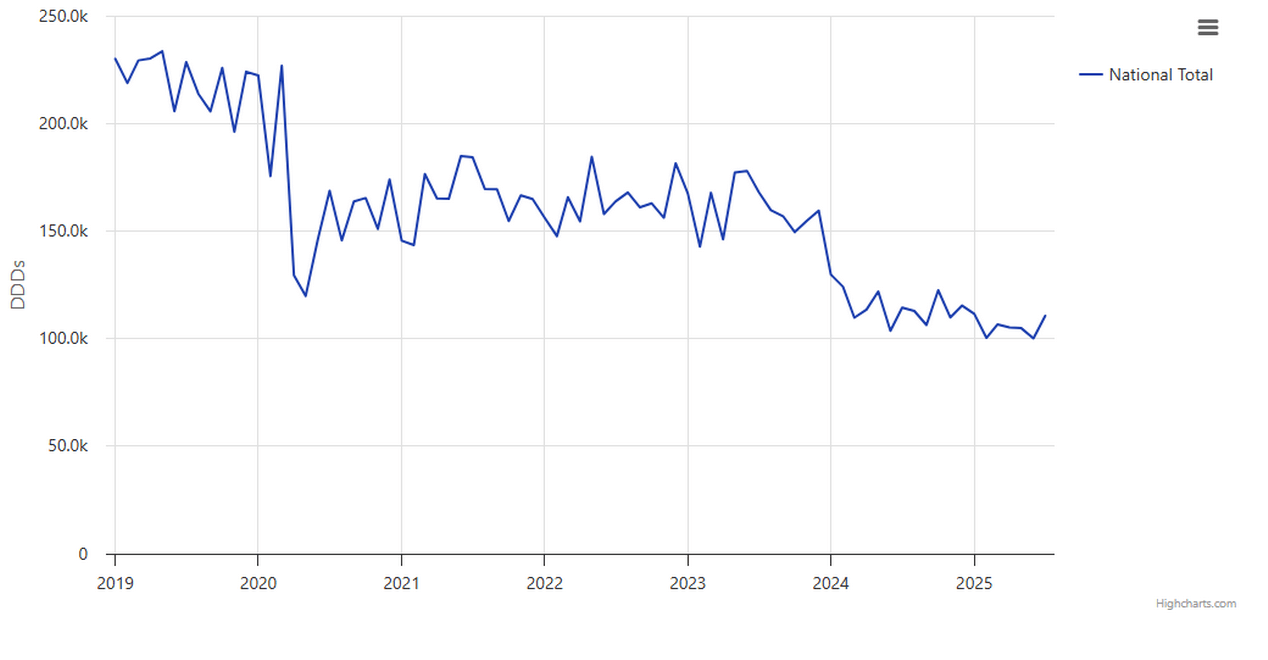
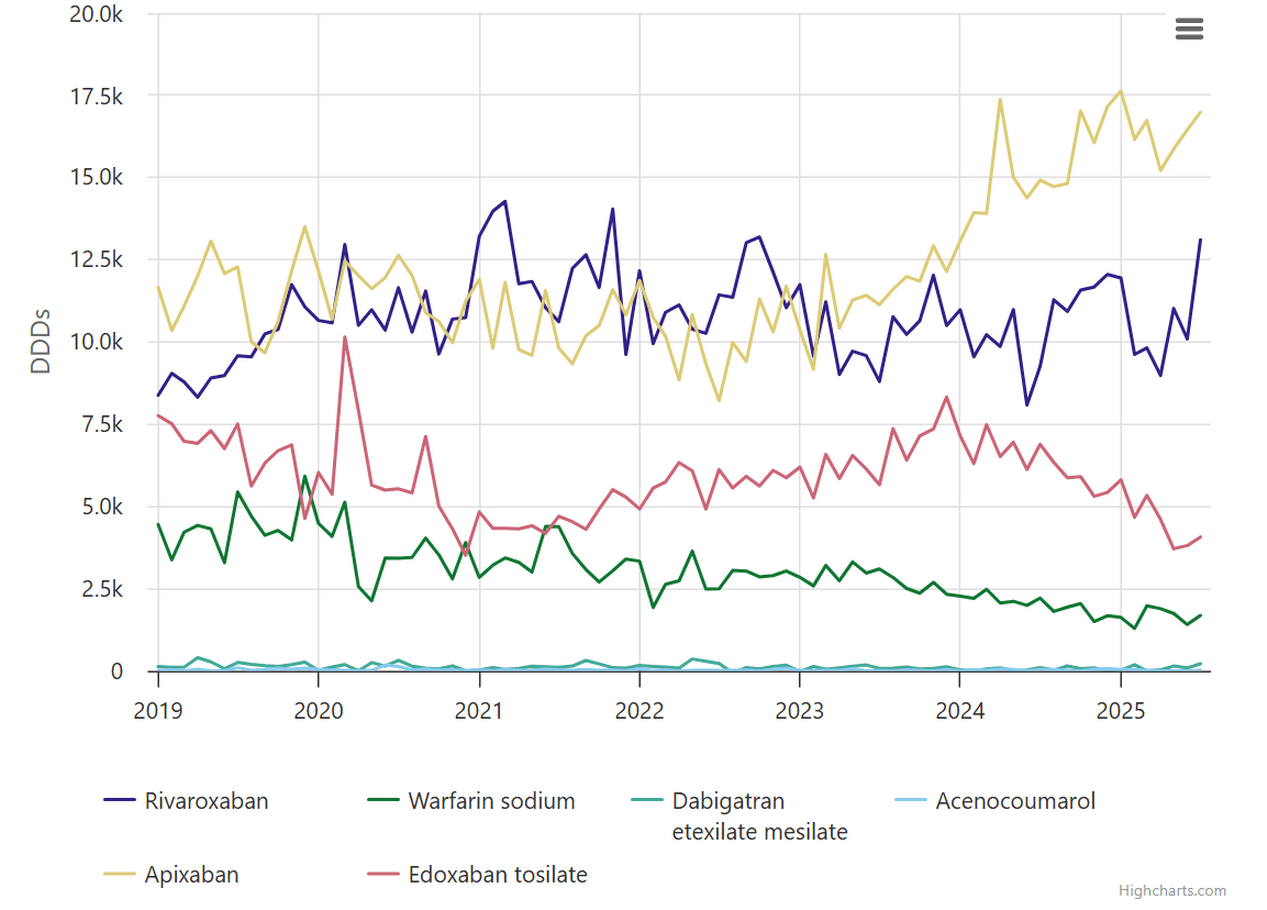
VKA vs direct oral anticoagulants in your organisation
NICE recommends direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) over VKAs for patients starting anticoagulation for stroke prevention in the context of atrial fibrillation. Using the multi-product search feature you can compare the use of warfarin, with each of the DOACs in your organisation. In this analysis, we can see a breakdown of each DOAC and VKA at a single NHS trust.
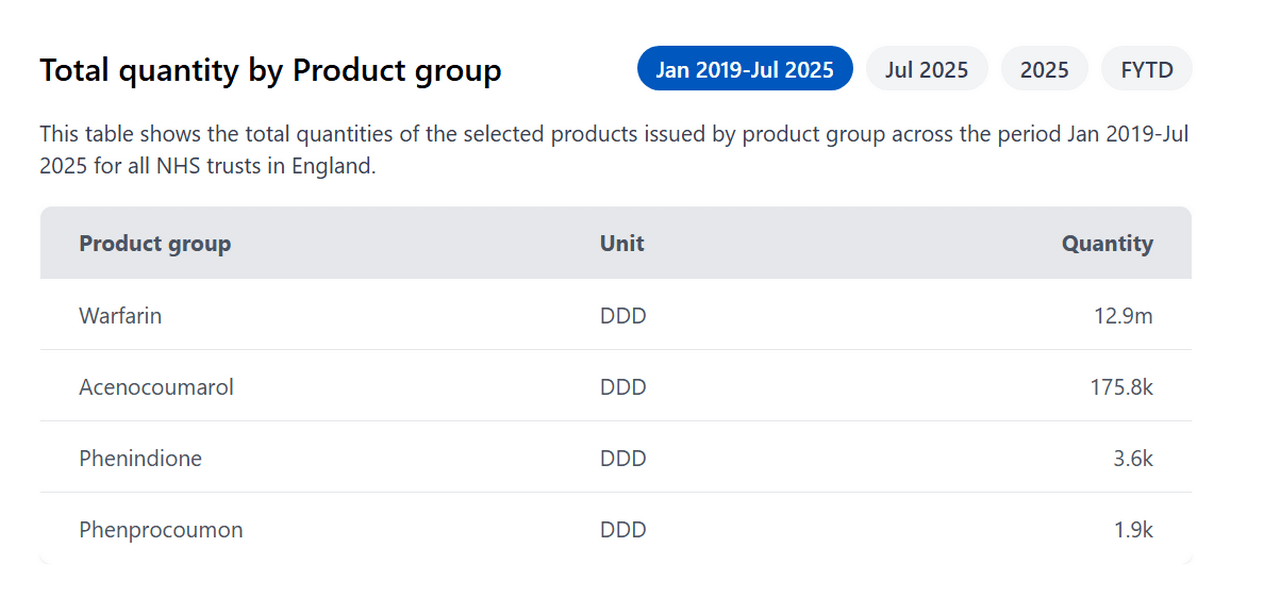
How often are the other VKAs issued in hospitals in England?
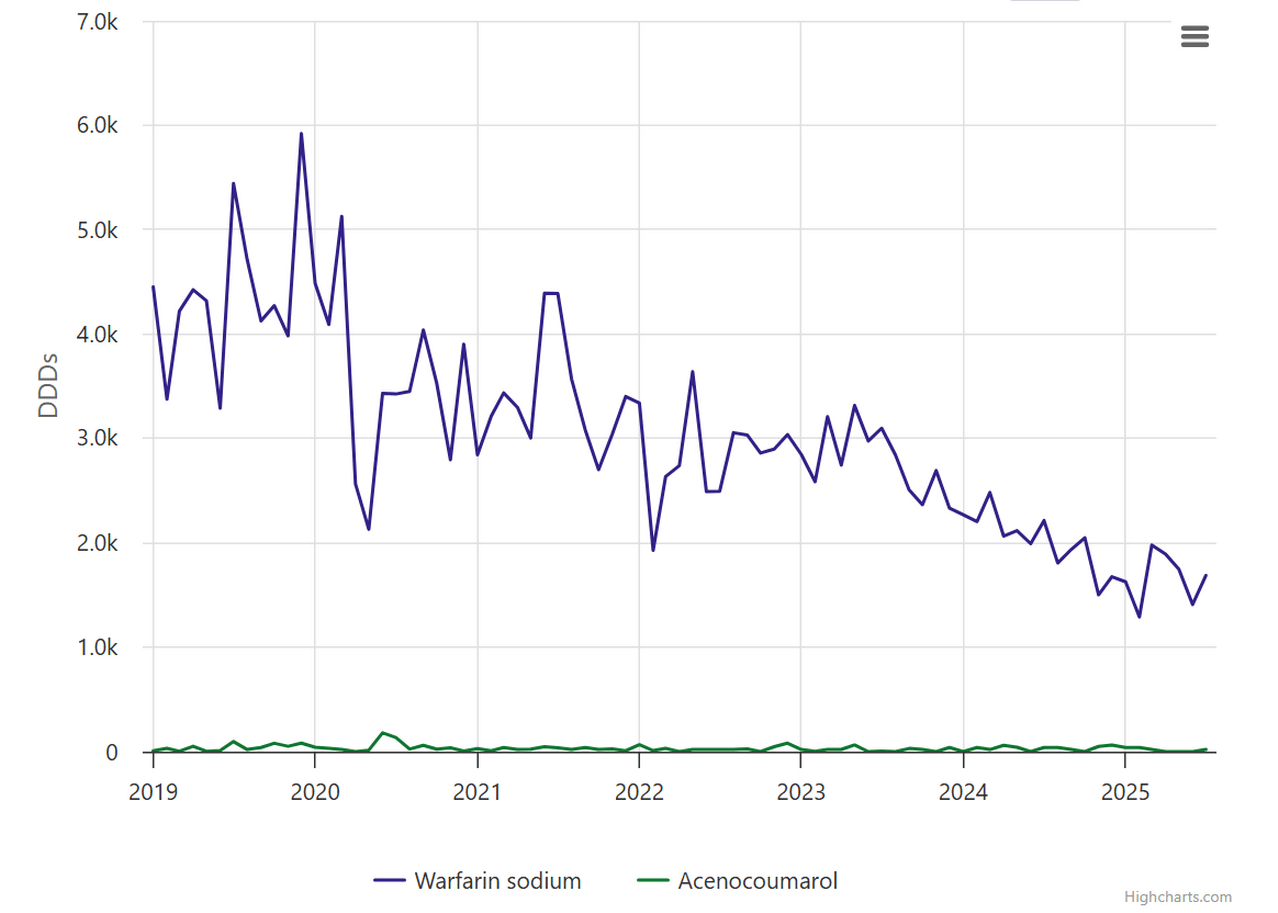
Whilst warfarin is the most commonly issued VKA, there are others in use in the NHS in England. Just like warfarin, they require frequent blood test monitoring and have a variable dose. To check whether other VKAs are used in your organisation you can use OpenPrescribing Hospitals. This analysis searches for all VKAs issued in all NHS trusts in England.
You can run the same search in individual hospitals to check use in your Trust.
Top tip for this analysis!
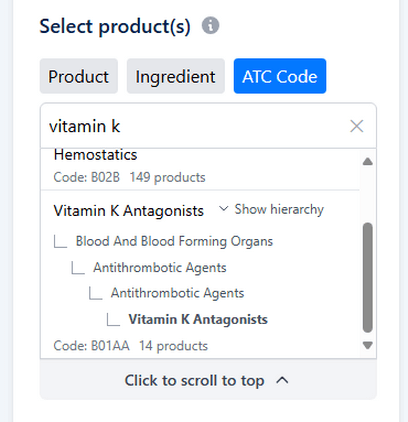
Find all medicines in a class using ATC codes
To find all medicines that belong to a certain class (ie all VKAs, all statins, all proton pump inhibitors), you can use anatomical therapeutic classification (ATC) codes. On the analysis builder, in the select product(s) section, select ATC code. The ATC classification system provides a classification for the active ingredients in medicines based on their anatomical (which organ or system they treat), therapeutic (what condition or disease they treat), pharmacological (how they work) and chemical properties (the structure and composition of the substance).
In this example, we searched for ‘vitamin K antagonists’.
This is helpful to include all medications within a class, even those you perhaps might not have thought of straightaway! For more on the use of ATC codes in OpenPrescribing Hospitals, you can read our post, Classifying and measuring medicines usage with the ATC/DDD system.
If you have any suggestions / comments / feedback for the platform OpenPrescribing Hospitals please get in touch at bennett@phc.ox.ac.uk.


